Summary
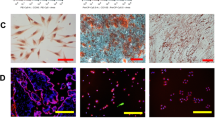
A cell-line was established from bovine placental cotyledon. When cultured in M199 with 10% fetal bovine serum, this cell-line had a doubling time of about 18 h. With immunohistochemistry, it was demonstrated that this cell-line expressed vimentin and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). While both molecules are expressed in endothelial cells, ACE is usually considered to be a specific marker for endothelial cells. Furthermore, cells were shown to take up Dil-Ac-LDL (acetylated low-density lipoprotein labeled with 1,1′-dioctadecyl-3,3,3′-tetramethylindo-carbocyanine perchlorate). This characteristic feature has been used to identify endothelial cells. Finally, when cultured on matrigel, this cell-line formed tube-like structures similar to those formed by endothelial cells. Tube-formation on matrigel is a physiological property specific to endothelial cells. In conclusion, these three lines of evidence strongly suggest that this cell-line is endothelial cell in nature. Further studies using an endothelial cell-line from bovine placenta may help to elucidate the cause of bovine placental retention, a major cause for economic loss in bovine industry. Furthermore, an endothelial cell-line could be an important tool in research areas such as tissue remodeling, angiogenesis, and cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auerbach, R.; Alby, L.; Grieves, J., et al. Monoclonal antibody against angiotensin-converting enzyme: its use as a marker for murine, bovine and human endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79:7891–7895; 1982.
Baatout, S.; Cheta, N. Matrigel: a useful tool to study endothelial differentiation Rev. Roum. Med. Int. 34:263–269; 1996.
Bassett, D. L. The changes in the vascular pattern of the ovary of the albino rat during estrous cycle. Am. J. Anat. 73:251–291; 1943.
Challier, J. C.; Kacemi, A.; Olive, G. Mixed culture of pericytes and endothelial cells from fetal microvessels of the human placenta. Cell. Mol. Biol. 41:233–241; 1995.
Craig, L. E.; Spelman, J. P.; Strandberg, J. D.; Zink, M. C. Endothelial cells from diverse tissues exhibit differences in growth and morphology. Microvasc. Res. 55:65–76; 1998.
Denekamp, J. Vasculature as a target for tumor therapy. In: Hammersen, F.; Hudicka, O., ed. Progress in applied microcirculation. Vol. 4. Karger: Basel; 1984;28–38.
Feng, S.; Peter, A. T.; Asem, E. K. Establishment of pure culture of distinct cell types from bovine placental cotyledon. Methods Cell Sci., in press.
Ferrell, C. L. Placental regulation of fetal growth. In: Campion, D. R.; Hausman, G. J.; Martin, R. J., ed. Animal growth regulation. New York: Plenum; 1989:1–10.
Folkman, J.; Klagsbrun, M. Angiogenic factors. Science 235:442–447; 1987.
Grant, D. S.; Tashiro, K.; Segui-Real, B.; Yamada, Y.; Martin, G. R.; Kleinman, H. K. Two different laminin domains mediate the differentiation of human endothelial cells into capillary-like structures in vitro. Cell 58:933–943; 1989.
Jaffe, E. A.; Nachman, R.; Becker, C.; Mimick, R. Culture of human endothelial cells. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J. Clin. Invest. 52:2745–2756; 1973.
Kacemi, A.; Challier, J.-C.; Graltier, M.; Olive, G. Culture of endothelial cells from human placental microvessels. Cell Tissue Res. 283:183–190; 1996.
Klagsbrun, M.; D'Amore, P.D. Regulators of angiogenesis. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 53:217–239; 1991.
Kleinman, H. K.; McGarvey, M. L.; Hassell, J. R.; Star, V. L.; Cannon, F. B.; Laurie, G. W.; Martin, G. R. Basement membrane complexes with biological activities. Biochemistry 25:312–318; 1986.
Kubota, Y.; Kleinman, H. K.; Martin, G. R.; Lawley, T. J. Role of laminin and basement membrane in the morphological differentiation of human endothelial cells into capillary like structures. J. Cell. Biol. 107: 1589–1598; 1988.
Madri, J. A.; Williams, S. K. Capillary endothelial cell cultures: phenotypic modulation by matrix components. J. Cell. Biol. 97:153–165; 1983.
Meegdes, B. H. L. M.; Ingenhoes, R.; Peeters, L. L. H.; Exalto, N. Early pregnancy wastage: relationship between chorionic vascularization and embryonic development. Fertil. Steril. 49:216–220; 1988.
Moll, R.; Franke, W. W.; Schiller, D. L.; Geiger, B.; Krepler, R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell 31:11–24; 1982.
Montesano, R.; Orci, L.; Vassalli, P. In vitro rapid organization of endothelial cells into capillary-like networks promoted by collagen matrices. J. Cell. Biol. 97:1648–1652; 1983.
Ono, M.; Izumi, H.; Yoshida, S., et al. Angiogenesis as a new target for cancer treatment. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 38:S78-S82; 1996.
Reynolds, L. P.; Killilea, S. D.; Redmer, D. A. Angiogenesis in the female reproductive system. FASEB J. 6:886–892; 1992.
Reynolds, L. P.; Redmer D. A. Secretion of angiogenic activity by placenta tissues of cows at several stages of gestation. J. Reprod. Fertil. 83: 497–502; 1988.
Rexroad, C. E.; Casida, L. E.; Tyler, W. J. Crown-rump length of fetuses in purebred Holstein-Friesian cows. J Dairy Sci. 57:346–347; 1974.
Taub, M.; Wang, Y.; Szcesney, T. M.; Keinman, K. Epidermal growth factor or transforming growth factor alpha is required for kidney tubulogenesis in matrigel cultures in serum-free medium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:4000–4002; 1990.
Voyta, J. C.; Netland, P. A.; Via, D. P.; Zetter, B. R. Specific labeling of endothelial cells fluorescent acetylated low density lipoprotein. J. Cell. Biol. 99:81A; 1984.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, S., Peter, A.T. & Asem, E.K. Endothelial-like cells from the bovine placental cotyledon. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 36, 527–531 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1290/1071-2690(2000)036<0527:ELCFTB>2.0.CO;2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1290/1071-2690(2000)036<0527:ELCFTB>2.0.CO;2